Tourism Sector in India: Current Landscape and Vision 2047

Introduction
“Every fifth job created in the world over the last decade has come from tourism.” India clearly shows this global trend. In 2023, India’s travel and tourism industry contributed nearly ₹19.13 trillion (US$232 billion) to the economy, which is about 5.9% of GDP, and supported over 43 million jobs. With over 2.5 billion domestic trips and 9.5 million foreign tourist arrivals, the sector is both a vital economic driver and a cultural bridge connecting India to the world.
Tourism is not just about leisure. It supports livelihoods in rural areas, empowers women, promotes heritage preservation, and boosts India’s influence globally. As India looks toward its centenary of independence in 2047, tourism is seen as one of the key areas for inclusive growth, sustainability, and global leadership.
Current Status of the Tourism Sector
Contribution to GDP
- The tourism sector’s total impact was ₹19.13 trillion, equivalent to approximately 9 to 10% of the GDP.
- It is one of the biggest contributors to India’s service economy.
Employment
- Tourism supported ~43 million jobs directly and nearly 76 million jobs indirectly, accounting for ~10% of the workforce Tourism Sector in India.
- Jobs span hospitality, handicrafts, transport, guides, homestays, and MSMEs.
Domestic Tourism
- Over 2.5 billion trips were recorded in 2023.
- Pilgrimage circuits (e.g., Varanasi, Tirupati, Ayodhya), hill stations, and wellness tourism were major drivers.
Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs)
- India welcomed ~18.9 million foreign tourists, with Taj Mahal, Rajasthan, Goa, Kerala, and the Golden Triangle remaining top draws.
- Post-pandemic recovery is strong, but still below leading destinations like France or Thailand.
Foreign Exchange Earnings (FEEs)
- Tourism generated ₹231,927 crore in foreign exchange.
Key Government Initiatives
- Incredible India 2.0 – branding and international campaigns.
- Dekho Apna Desh – promotion of domestic circuits.
- Swadesh Darshan – theme-based circuits (spiritual, Buddhist, coastal, tribal).
- UDAN scheme – improving regional air connectivity.
| Indicator | Current Status (2023) | Vision 2047 Target |
| Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) | ~18.9 million | 50–60 million annually (Top 5 globally) |
| Domestic Tourist Visits | ~2.5 billion | 5+ billion annual visits with better regional spread |
| Tourism Contribution to GDP | ~INR 19 trillion (~9–10% of GDP) | 12–15% of GDP |
| Employment | ~40–43 million jobs | 100+ million jobs (direct + indirect) |
| Foreign Exchange Earnings (FEEs) | ~₹231,927 crore | 4–5× growth through high-value tourism |
| Iconic Destinations | ~20 major global sites | 100+ world-class destinations |
| Digital Readiness | Expanding e-visa, digital ticketing | Full Digital India Travel Stack (AI, AR/VR, multilingual apps) |
| Sustainability | Early initiatives in eco-tourism, green hotels | Carbon-neutral tourism sector, strong ecosystem protection |
| Inclusivity | Growing rural/homestay programs | Tourism as a mass livelihood driver (women, youth, rural) |
Tourism in India: Current vs. Vision 2047 Targets
Tourism is one of the fastest-growing sectors in India. It plays a significant role in economic growth, job creation, and cultural exchange. In 2023, India’s tourism industry generated nearly 9 to 10% of GDP and supported over 40 million jobs. It attracted both domestic and international visitors to its rich heritage, natural beauty, and cultural diversity. Looking ahead, Vision 2047 aims to place India among the world’s top five tourist destinations. The focus will be on sustainability, inclusivity, and digital transformation.
Below is a detailed analysis of the sector’s current status and Vision 2047 targets:
Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs)
- Current Status (2023): India welcomed around 18.9 million foreign tourists, showing a strong recovery after the pandemic. Popular attractions like the Taj Mahal, Jaipur, Kerala, Goa, and the Golden Triangle remain key parts of foreign travel plans.
- Vision 2047 Target: By 2047, India wants to attract 50 to 60 million foreign tourists each year, aiming to be among the top five global destinations. This will need increased international marketing, improvements in infrastructure, and easier visa and travel connections.
Domestic Tourist Visits
- Current Status (2023): With a growing middle class, India saw 2.5 billion domestic tourist visits, highlighting the sector’s strength and cultural variety. Domestic travellers play an important role in boosting local economies, especially in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- Vision 2047 Target: Domestic visits are expected to top 5 billion each year, with efforts to extend tourism benefits beyond traditional hotspots to include lesser-known places like Northeast India, tribal areas, and heritage towns.
Tourism Contribution to GDP
- Current Status (2023): The sector added nearly INR 19 trillion (about 9 to 10% of GDP, total impact), making it a leading driver of India’s service economy.
- Vision 2047 Target: By 2047, tourism is projected to contribute 12 to 15% of GDP. This increase will reflect not only a rise in volume but also a shift toward high-value experiences like luxury travel, medical tourism, eco-tourism, and wellness retreats.
Employment Generation
- Current Status (2023): Tourism supports around 40 to 43 million jobs in areas like hospitality, transport, food services, guiding, handicrafts, and informal sector jobs.
- Vision 2047 Target: The sector expects to create over 100 million jobs, especially for youth, women, and rural communities. Skill development programs under initiatives like PM Vishwakarma Yojana and Skill India will be essential.
Foreign Exchange Earnings (FEEs)
- Current Status (2023): India earned about ₹231,927 crore in foreign exchange from tourism.
- Vision 2047 Target: With a stronger global presence, the sector aims to increase FEEs by four to five times, focusing on high-spending international tourists through premium offerings in medical, spiritual, and adventure tourism.
Iconic Destinations
- Current Status (2023): India has around 20 globally recognised destinations, including the Taj Mahal, Jaipur, Goa, Kerala backwaters, Ladakh, and Varanasi.
- Vision 2047 Target: By developing over 100 world-class destinations, India will enhance its offerings with better infrastructure, branding, and facilities that meet global standards to compete with countries like France, Italy, and Thailand.
Digital Readiness
- Current Status (2023): The growth of e-visas, online ticket booking, and digital payments has made travel easier. Apps for train and flight bookings, as well as state tourism, are becoming more popular.
- Vision 2047 Target: By 2047, India plans to create a complete Digital Travel Stack that includes AI-based recommendations, AR/VR immersive tours, real-time translation apps, and user-friendly multilingual platforms, ensuring a smart experience for tourists.
Sustainability
- Current Status (2023): Initial steps in eco-tourism, green hotels, and responsible travel are showing up, but mass tourism is still putting pressure on fragile ecosystems like the Himalayas and coastal areas.
- Vision 2047 Target: India aims to build a carbon-neutral tourism ecosystem, where green hotels, sustainable transport, waste management, and biodiversity conservation are core parts of tourism planning.
Inclusivity
- Current Status (2023): Initiatives like rural tourism, homestays, and handicrafts promote community-based tourism. Women and local artisans are beginning to see benefits, but opportunities are still limited.
- Vision 2047 Target: Tourism will serve as a significant source of income, bringing women, rural youth, and marginalised groups into the tourism economy. Policies will promote fair growth, bridging rural and urban gaps while preserving cultural heritage.
State-wise Contributions and Projections to 2047
Tourism growth in India largely depends on the states. Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh are the biggest contributors to domestic visits. To better understand future trends, we model three growth scenarios: Low (3% CAGR), Moderate (5% CAGR), and High (7% CAGR). These scenarios run from 2023 to 2047.
State-wise Tourist Visits Projections (Millions)
| State | Baseline (2023) | 2047 (3% CAGR) | 2047 (5% CAGR) | 2047 (7% CAGR) |
| Uttar Pradesh | 478 | 940 | 1,540 | 2,520 |
| Tamil Nadu | 286 | 562 | 922 | 1,510 |
| Karnataka | 284 | 558 | 915 | 1,500 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 194 | 381 | 625 | 1,030 |
| Maharashtra | 156 | 306 | 500 | 820 |
| Rajasthan | 150 | 294 | 480 | 790 |
| Other States | 952 | 1,870 | 3,050 | 5,000 |
| Total | 2,500 | 4,911 | 8,032 | 12,670 |
Tourism GDP and Employment Projections (National Level)
| Growth Scenario | Tourism GDP 2023 (₹ lakh crore) | 2047 Tourism GDP (₹ lakh crore) | Jobs Supported 2023 (mn) | Jobs by 2047 (mn) |
| 3% CAGR | 2.05 | 4.15 | 76.2 | 154 |
| 5% CAGR | 2.05 | 6.12 | 76.2 | 231 |
| 7% CAGR | 2.05 | 9.70 | 76.2 | 365 |
Vision 2047: Ambitious Targets
The Vision 2047 roadmap, crafted by FAITH and the Ministry of Tourism, lays out bold goals:
Economic & Employment Targets
- Contribution to GDP: 12–15% by 2047.
- Employment: 100–200 million jobs (direct & indirect).
- Tourism GDP could reach $1–2 trillion by 2047, depending on the growth rate Tourism Sector in India
Visitor Targets
- Domestic visits: 5+ billion annually.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals: 50–60 million (Top-5 globally).
Infrastructure & Destinations
- Develop 100+ world-class destinations.
- Upgrade airports, highways, and smart cities linked to tourism.
Digital Transformation
- AI-driven travel apps with multilingual support.
- AR/VR immersive experiences at heritage sites.
- Seamless Digital India Travel Stack (smart payments, e-tickets).
Inclusivity & Sustainability
- Eco-tourism and carbon-neutral hubs.
- Expansion of homestays, rural circuits, and women-led enterprises.
- Focus on community-based models, similar to Kerala’s Responsible Tourism Mission.
Budget 2025–26: A Turning Point
The Union Budget 2025–26 provided a significant boost:
- ₹2,541 crore allocation to the Ministry of Tourism (3× increase).
- 50 Destination Challenge – develop 50 globally competitive hubs.
- MSME & homestay support – MUDRA loans, credit guarantees.
- Skill-building – ₹60 crore for training under Hunar Se Rozgar Tak.
- Visa reforms – expanded e-visas, reduced fees, promotion of Heal in India.
- Cultural heritage digitisation – 1 crore manuscripts to be digitised for cultural tourism.
Challenges & Risks
Overtourism
- Taj Mahal, Shimla, and Ladakh face carrying-capacity strain.
- Seasonal overcrowding affects ecosystems and visitor experience.
Climate Change
- Flash floods in Himachal (2023), Kerala floods (2018), and coastal erosion in Goa highlight vulnerabilities.
Infrastructure Gaps
- Last-mile connectivity and sanitation remain weak at several pilgrimage and heritage sites.
- Skill Shortages: Many guides and homestay operators lack formal training.
- Inconsistent language skills reduce competitiveness in global markets.
Security & Policy
- Barriers: Permit regimes in Northeast India restrict inbound flows.
- Periodic unrest in Kashmir impacts international arrivals.
Policy Responses and Recent Government Initiatives
To achieve the ambitious Tourism Vision 2047, the Government of India has rolled out several policy measures aimed at strengthening infrastructure, branding, skills, and sustainability. Key initiatives include:
Infrastructure Support through SASCI
The Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (SASCI) scheme provides central assistance for upgrading iconic tourist centres and supporting state-level projects. The funding helps build last-mile connectivity, modern amenities, and globally competitive tourist hubs. For instance, projects include heritage site upgrades, eco-friendly facilities, and smart infrastructure.
Marketing and Facilitation
The government continues to promote India globally through the flagship “Incredible India” campaign, showcasing heritage, spirituality, and modern attractions. At the same time, the e-Visa facility has been expanded to more than 170 countries, significantly improving ease of travel. Complementary reforms, such as simplified immigration and airport processes, are also in progress. These steps make India more accessible and appealing to international travellers.
Skill Development and Capacity Building
Tourism being a service-intensive sector, the Ministry of Tourism has launched several programs for hospitality training, tour guide certification, and entrepreneurship support. Initiatives under the Capacity Building for Service Providers (CBSP) and Hunar Se Rozgar Tak (HSRT) schemes aim to upskill India’s workforce to global service standards, ensuring better tourist experiences while generating employment.
Sustainability and Product Diversification
Recognising the challenges of over-tourism and ecological stress, India is promoting eco-tourism zones, rural/community-based tourism, and off-season travel circuits. Programs emphasise homestays, cultural immersion, and eco-friendly facilities to balance growth with sustainability. These initiatives not only reduce pressure on overcrowded hotspots like Agra and Goa but also channel tourism benefits to rural and tribal communities.
Conclusion: Tourism as India’s Soft Power by 2047
India’s tourism story goes beyond economic numbers. It involves cultural diplomacy, job creation, and sustainability. By 2047, if India maintains over 6% annual growth, the sector could become a $1 trillion industry, supporting more than 200 million jobs.
With the right mix of policy changes, infrastructure improvements, digital innovation, and sustainable practices, India can make tourism a key factor in its global leadership. This would showcase not only economic strength but also its rich heritage, diversity, and hospitality.
As the world seeks authentic, sustainable, and enriching travel experiences, India in 2047 has the potential to be one of the world’s top five tourist destinations. It can redefine tourism as a source of inclusive prosperity and cultural leadership.
The Indo-Pacific: A Geoeconomic and Strategic Epicenter
The Indo-Pacific has become the world’s most dynamic economic region. It is home to over…
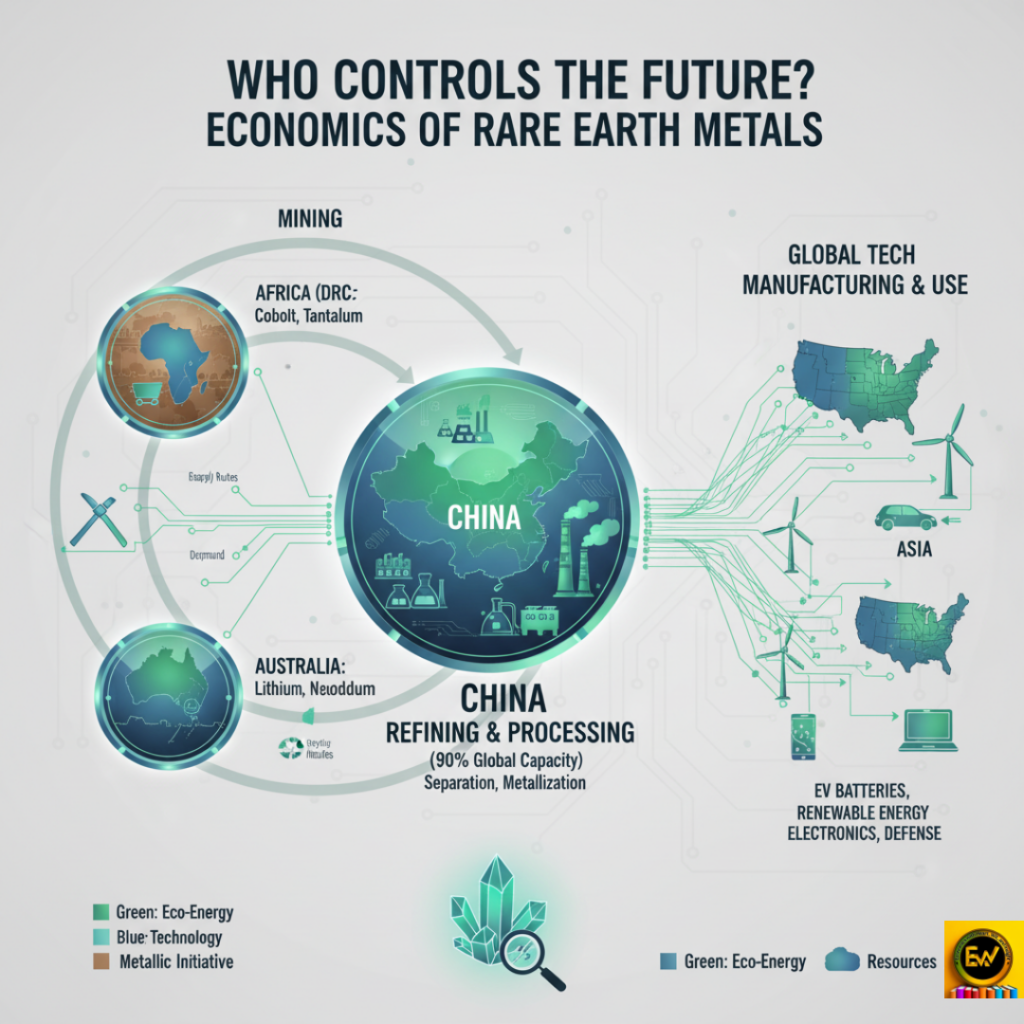
Economics of Rare Earth Metals
Rare earth elements and critical minerals are vital for clean energy and technology. They form…
Indian Rupee Depreciation Against the US Dollar
Introduction In recent years, the Indian Rupee has undergone significant depreciation against the US Dollar,…
Green Economy: Can India Balance Growth with Climate Goals?
India stands at a crucial point in history. As the world’s most populous nation and…
“Understanding ‘67’: The Viral Gen Alpha Slang That Became Word of the Year 2025”
Source – The Economic Times Every year, Dictionary.com selects a term that captures the spirit…
BRICS Expansion 2025: Can It Challenge the Dollar’s Dominance?
The BRICS bloc, which includes Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, has been evolving…






I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/el/register?ref=DB40ITMB
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/ES_la/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/id/register?ref=UM6SMJM3