India’s 100-Day Reform Plan: Unlocking Growth and Investment

India’s 100-day reform plan represents a landmark economic strategy aimed at reshaping the country’s growth trajectory. Announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and deliberated with top ministers. NITI Aayog members and the Economic Advisory Council, this reform blueprint has been crafted at a time when the global economy faces multiple disruptions. These include slowing growth, trade wars, high inflation, and geopolitical conflicts. For India, this plan signals a decisive push toward modernising regulations, enhancing business competitiveness, and creating new opportunities for investors and entrepreneurs.
The reform package is ambitious in its scope. It covers key aspects such as FDI liberalisation, tax simplification, export promotion, and industry-specific reforms. And the establishment of a Task Force dedicated to next-generation policy design. With its focus on ease of doing business, protecting startups, and cutting compliance burdens. The plan aligns with India’s long-term vision of becoming a developed nation by 2047. In the following sections. We provide a detailed analysis of each reform and its potential economic impact. And why it matters for India’s growth journey. Additional charts, graphs, and infographics are included to illustrate the magnitude of change expected from these
reforms.
Easier FDI Rules
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has been one of the strongest drivers of India’s growth story over the past decade. However, the rules imposed during the COVID-19 period, particularly on countries sharing a border with India, slowed down inflows. While the restrictions were aimed at preventing hostile takeovers during economic vulnerability, they also discouraged genuine investments. The new 100-day reform blueprint suggests a calibrated relaxation of these restrictions. This would not mean an uncontrolled opening but rather a balanced framework where national interests are safeguarded while simultaneously welcoming strategic investments.Such reforms are particularly crucial for sectors like semiconductors, renewable energy, and advanced manufacturing, where India aims to become globally competitive.
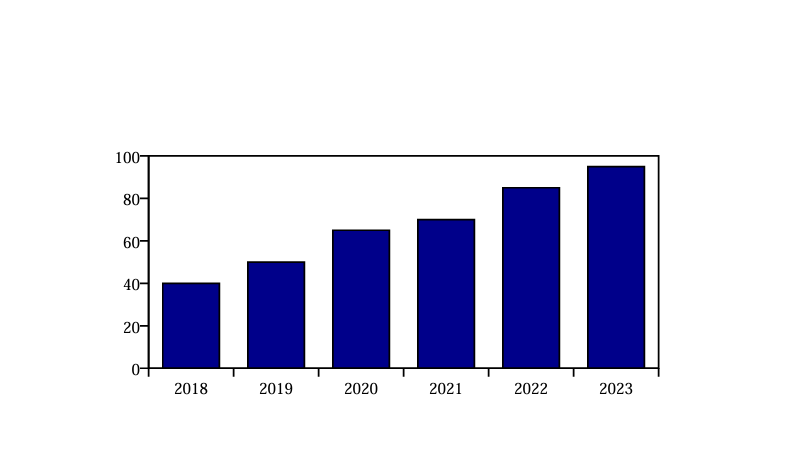
Support for Startups
India’s startup ecosystem is the third largest in the world, with thousands of companies spanning technology, healthcare, fintech, edtech, and green energy. Yet, compliance hurdles, complex tax rules, and a lack of early-stage funding have constrained many smaller ventures. The reform plan proposes to tackle these bottlenecks by offering tax breaks for innovative startups, reducing GST on SaaS products, and simplifying the process of raising venture capital. This can help unleash the next wave of unicorns while creating jobs for millions.
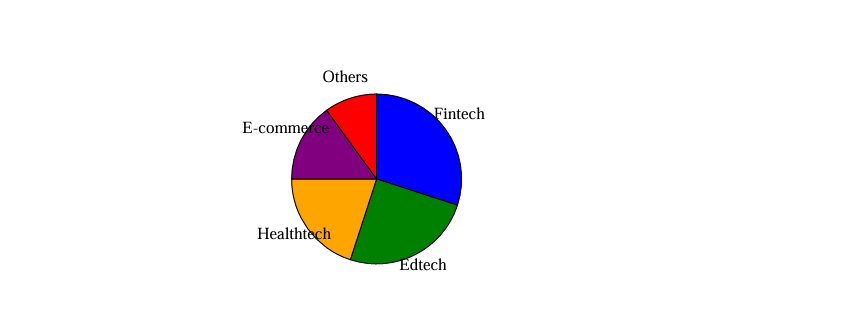
GST Overhaul
The Goods and Services Tax, introduced in 2017, was hailed as a game-changer for India’s fragmented tax system. However, the current structure—with multiple slabs of 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%— has created confusion. Businesses often complain about compliance costs and filing difficulties. The government now proposes to rationalise the GST structure, possibly merging slabs and lowering taxes on essential goods. This could boost consumption, as lower prices encourage household spending. Moreover, digital compliance tools will make filing simpler for small businesses. Over time, this overhaul is expected to enhance efficiency in tax collection and increase consumer satisfaction.
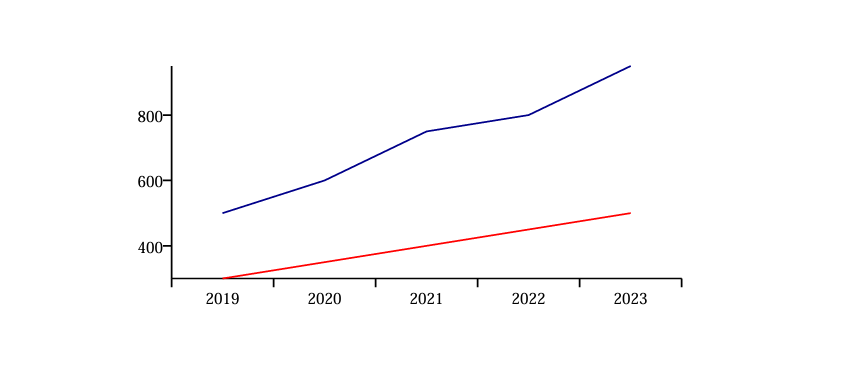
Boosting Exports and Global Supply Chains
Exports are a critical engine of India’s economy. The reform plan emphasises easing restrictions on e-commerce exports and simplifying certification procedures. With global trade expected to face disruptions due to tariff wars, India must position itself as a reliable hub for high-quality goods. By streamlining logistics, investing in port infrastructure, and everaging trade agreements, the government hopes to double exports within the next decade. A focus on electronics, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy equipment could cement India’s role in global supply chains.
The Task Force on Next-Generation Reforms
Perhaps the most significant component of the 100-day plan is the creation of a Task Force that will audit existing laws, regulations, and compliance systems. Unlike previous committees, this Task Force will work with a mandate to cut unnecessary procedures, reduce costs for businesses, and recommend modern frameworks aligned with Digital India. The Task Force will also ensure legal protection for startups and SMEs against arbitrary actions, thus boosting confidence in entrepreneurship. Its work will be crucial for creating a predictable, transparent, and investor-friendly environment.
Conclusion
India’s 100-day reform plan is more than just a short-term economic stimulus. It is a transformative agenda aimed at creating a future-ready economy. By focusing on FDI reforms, startup support, tax simplification, export promotion, and governance modernisation. The government has laid down a foundation for sustainable growth. If executed with precision, these reforms could not only accelerate India’s GDP growth. But also make the country a global leader in innovation and industry. For businesses, it means lower costs and better opportunities; for consumers, cheaper goods and services; and for the nation, a path toward prosperity by 2047.
The Indo-Pacific: A Geoeconomic and Strategic Epicenter
The Indo-Pacific has become the world’s most dynamic economic region. It is home to over…
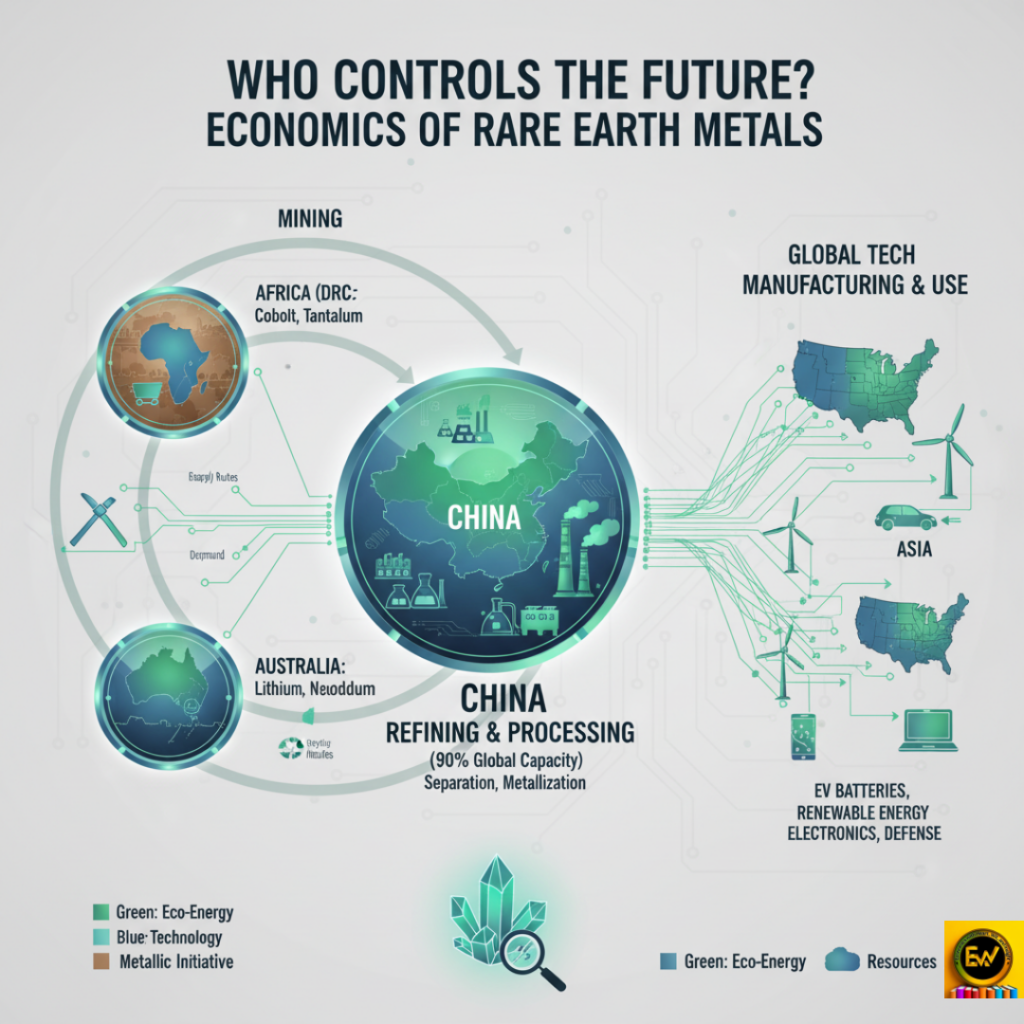
Economics of Rare Earth Metals
Rare earth elements and critical minerals are vital for clean energy and technology. They form…
Indian Rupee Depreciation Against the US Dollar
Introduction In recent years, the Indian Rupee has undergone significant depreciation against the US Dollar,…
Green Economy: Can India Balance Growth with Climate Goals?
India stands at a crucial point in history. As the world’s most populous nation and…
“Understanding ‘67’: The Viral Gen Alpha Slang That Became Word of the Year 2025”
Source – The Economic Times Every year, Dictionary.com selects a term that captures the spirit…
BRICS Expansion 2025: Can It Challenge the Dollar’s Dominance?
The BRICS bloc, which includes Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, has been evolving…







Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/pt-PT/register-person?ref=KDN7HDOR
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/si-LK/register?ref=LBF8F65G
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/es-AR/register-person?ref=UT2YTZSU
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/de-CH/register-person?ref=W0BCQMF1